Roles of Sensory Memory in Learning


Why is sensory perception crucial in learning?
Have you ever wondered how your brain decides what to focus on in a bustling classroom or during a quiet study session? Sensory perception is fundamental to human cognition, acting as a gateway to our awareness and understanding of the world. It enables us to process incoming sensory information and navigate our environment effectively, underpinning many aspects of cognitive processing and learning outcomes.
Temporary storage of sensory input
- Function Sensory perception acts as a temporary storehouse for incoming sensory information, allowing individuals to perceive and become aware of their surroundings by holding sensory input for a brief period.
- Example Consider how you might glance at a clock without initially noting the time; sensory memory retains the image long enough for you to decide to look back and consciously register the time.
Directs selective attention
- Function It guides selective attention by briefly holding sensory information before it is processed further, helping individuals focus on relevant stimuli while filtering out distractions.
- Example In a noisy classroom, sensory memory helps a student focus on the teacher’s voice, ignoring irrelevant sounds like the rustling of papers or whispers from classmates.
Integrates multisensory experiences
- Function Integrates information from multiple sensory modalities—sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell—facilitating the synthesis of multisensory experiences.
- Example When learning to cook a new dish, integrating the textures, scents, and tastes can enhance understanding and retention of the cooking techniques and ingredients.
- Example In a noisy classroom, sensory memory helps a student focus on the teacher’s voice, ignoring irrelevant sounds like the rustling of papers or whispers from classmates.
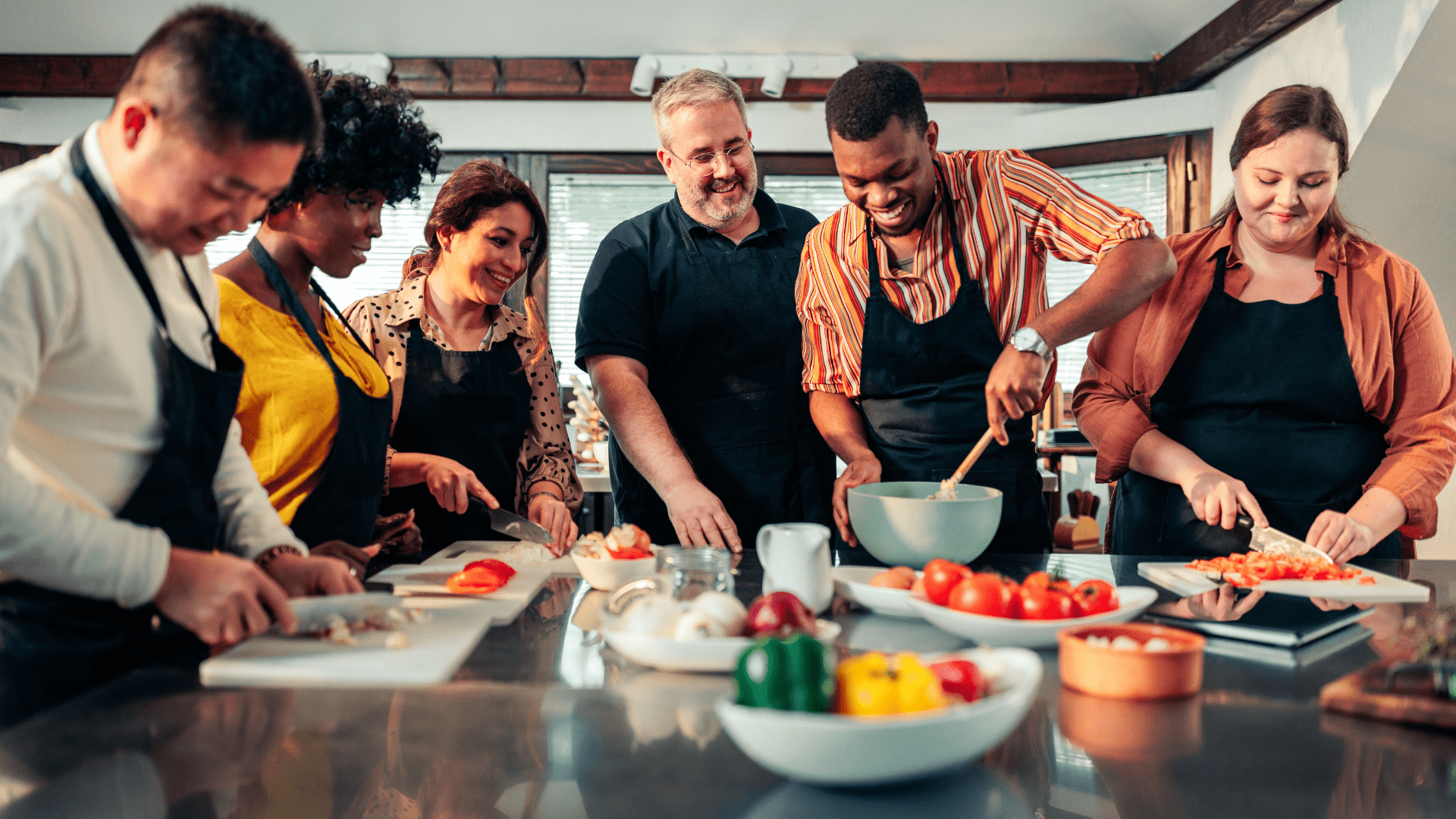


Enhances learning and memory
- Empirical support Research shows that sensory perception is crucial for the encoding process, facilitating the transfer of sensory input to short-term and then long-term memory, thereby enhancing learning and retention. Studies have demonstrated that students taught with multisensory approaches have higher retention rates compared to those taught with traditional methods.
For example, the study of Esplendori et. al. (2023) evaluates the integration of the Multisensory Integration Approach Model with the Learning Assimilation Theory and Bloom’s Cognitive Process Domain to enhance lesson planning for teaching Acute Coronary Syndrome to nursing undergraduates. It demonstrates that using a multisensory approach, which includes pre-organized or recall activities that stimulate various senses aligned with instructional objectives, can significantly improve the reception and processing of educational content. For further information, read Multisensory integration approach.
- Practical application We can use tools like interactive multimedia that combine audio, visuals, and tactile interaction to leverage sensory memory, enhancing student engagement and memory retention.
Creating multisensory learning environments
- Strategy Use aromatic elements during a history lesson about the spice trades to engage olfactory senses, or employ tactile maps in geography to enhance spatial understanding.
- Interactive component Experiment with integrating various sensory stimuli in a single lesson and observe the impact on student engagement and understanding.
Recognizing the importance of sensory perception in learning allows us to design engaging and effective instructional experiences. By leveraging multisensory approaches and creating enriched learning environments, we can harness the power of sensory perception to optimize learning outcomes and foster holistic cognitive development. Consider how you can incorporate these insights into your teaching strategy to cater to diverse learning styles and promote a deeper understanding among all students.